Secured NAT router
| Threat | Solution |
|---|---|
| Default exploits | Flash OpenWRT/pfSense |
| Weak firewall | Default-deny + IP whitelisting |
| Brute-force SSH | Key auth + fail2ban |
| Remote attacks | VPN-only access |
| ARP spoofing | DAI (if managed switch) |
A second NAT router can be used on the internal LAN to create a second, more secure LAN.
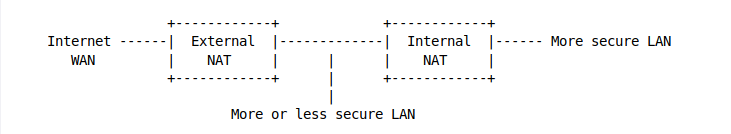
Benefits
Machines on the more-or-less-secure internal LAN can access the internet, but they are protected by the External NAT from most malwares.
Machines on the more-secure internal LAN can also access the internet, first by going out through the Internal NAT and then the External NAT.
Because the more-or-less-secure internal LAN is on the WAN side of the Internal NAT, machines on the more-or-less-secure internal LAN are unable to freely access the machines on the more-secure LAN behind the Internal NAT. Machines behind the Internal NAT can access the machines in the middle, but NOT the other way around.
When and where is this useful?
For isolating a router’s Demilitarised Zone (DMZ) network and servers.
Isolating an open or low-security wireless access point.
Protecting one ‘’high-value’’ machine from the rest of the network.
Flash custom firmware (Replace stock OS)
Stock router firmware often has unpatched vulnerabilities. Replace it with a security-focused OS:
Recommended Firmware Options:
| Firmware | Best For | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| OpenWRT | Most routers | Firewall, VPN, IDS, QoS |
| DD-WRT | Broadcom-based routers | VLANs, VPN, advanced NAT |
| pfSense | (x86 routers) | High security Enterprise firewall, IDS/IPS |
| OPNsense | User-friendly | Modern UI, Zenarmor (NGFW) |
Installation Steps
Check compatibility on the firmware’s website (e.g., OpenWRT Table of Hardware).
Backup stock firmware (in case of rollback).
Flash via TFTP/recovery mode (varies by router).
Reset to defaults after flashing.
Harden the firewall
Default-Deny policy
Block all inbound traffic (only allow replies to outbound requests):
# OpenWRT (via `uci`)
uci set firewall.@defaults[0].input="REJECT"
uci set firewall.@defaults[0].output="ACCEPT"
uci set firewall.@defaults[0].forward="REJECT"
uci commit && service firewall restart
Restrict LAN → Router access
Allow only admin IPs to access the router’s admin panel:
# OpenWRT example (allow only 192.168.1.100)
uci add firewall rule
uci set firewall.@rule[-1].src='lan'
uci set firewall.@rule[-1].dest_port='80,443,22'
uci set firewall.@rule[-1].proto='tcp'
uci set firewall.@rule[-1].target='ACCEPT'
uci set firewall.@rule[-1].src_ip='192.168.1.100'
uci commit && service firewall restart
Block WAN ping & scans
Disable ICMP (ping) and stealth-mode the router:
uci set firewall.@rule[0].enabled="0" # Disable ping
uci commit && service firewall restart
Secure Router access
Change default credentials
Set a strong password (use pwgen 16 1 for a random one).
Disable default admin accounts (e.g., admin:admin).
Enable SSH (With Key Auth)
Generate SSH keys on PC:
ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -f ~/.ssh/router_key
Copy the public key to the router:
ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/router_key.pub root@192.168.1.1
Disable password login:
uci set dropbear.@dropbear[0].PasswordAuth="off"
uci commit && service dropbear restart
Restrict Web Admin access
Allow only via LAN/VPN (disable WAN access):
uci set uhttpd.main.listen_http="192.168.1.1:80"
uci set uhttpd.main.listen_https="192.168.1.1:443"
uci commit && service uhttpd restart
Enable VPN-Only remote access
Instead of exposing the router to the internet, require VPN access:
Set Up WireGuard (OpenWRT)
Install WireGuard:
opkg install wireguard-tools
Generate keys:
wg genkey | tee privatekey | wg pubkey > publickey
Configure /etc/config/network:
config interface 'wg0'
option proto 'wireguard'
option private_key '<PRIVATE_KEY>'
list addresses '10.0.0.1/24'
config wireguard_wg0
option public_key '<CLIENT_PUBKEY>'
option allowed_ips '10.0.0.2/32'
Block All WAN admin access
Ensure no ports (22, 80, 443) are forwarded to the router.
Monitor & log attacks
Enable logging
Log firewall drops (OpenWRT):
uci set firewall.@defaults[0].log="1"
uci commit && service firewall restart
View logs:
logread -f | grep firewall
Intrusion Detection (Snort/Suricata)
Install on OpenWRT/pfSense:
opkg install suricata
suricata -c /etc/suricata/suricata.yaml -i br-lan
Physical security
Disable unused ports (USB, Telnet, FTP).
Place in a locked cabinet (prevents tampering).